Shell and Tube or Plate Heat Exchangers?

If you've ever researched liquid cooled products you may have come across two options, shell and tube or plate heat exchangers. Both the Shell and Tube and Plate Type heat exchangers work with the same principles, exchanging heat between two fluids through thermal conduction, but with very different construction methods. Deciding which is best for you can be difficult if you don't understand the benefits of either design.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Consisting of a bundle of small tubes within a large cylinder (or shell;) Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are a simple but effective construction, the principals of which have been around for well over 100 years (see the construction of a steam engine boiler for an example). They can be made at a low cost, even with low volumes, due to their simplicity and flexibility. They are ideal for applications where regular maintenance and servicing is required, such as in a marine environment, as most designs are easy to dismantle.
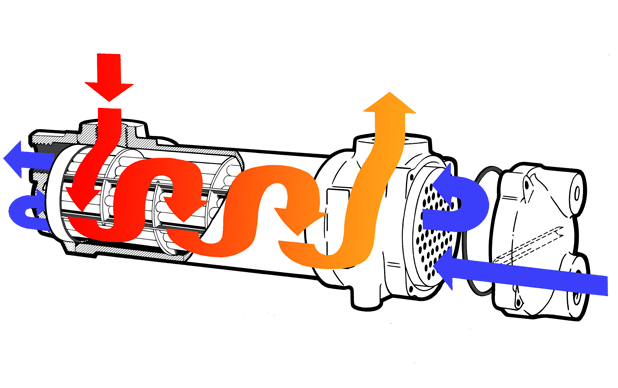
Advantages of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers;
- Smaller designs can be lower cost
- Much easier to service
- O Ring seals also make them cheap to service
- A better solution for sea water coolant, or other fluids at risk of clogging in narrow spaces
- Can provide better installation options (three pass, two pass header configurations etc.)
- Ideal solution for hydraulic power packs, mining machinery, sea water cooled vessels and swimming pool heating.
Plate Heat Exchangers
Although the principals of Plate Heat Exchangers are very similar to Shell and Tube the construction is very different. Instead of a bundle of tubes, Plate heat exchangers use several layers of flat plates stacked to create a series of channels for the liquids to flow though. They can often be more compact and sometimes lower cost than shell and tube, but do not have as much design flexibility as Shell and Tube. Their full stainless steel construction however does make them ideal for applications such as food processing and pharmaceutical production.
Advantages of Plate Heat Exchangers;
- More compact design
- A lower cost option wherever stainless steel is required
- Higher operating pressure capabilities
- Higher temperature capabilities
- Ideal for small district heating, beverage cooling, food and pharmaceutical production and low duty oil cooling applications.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are still the preferred option for many engineers due to the ease of servicing and their compatibility for use with sea water coolants. If you want to use a plate heat exchanger with sea water then it must be a gasketed plate pack with plates made from Titanium, so the cost is often higher than the equivalent shell and tube (even with Titanium tubes!)
Fortunately at Thermex we can supply either option, so if you are still uncertain which is better for you then please don't hesitate to contact us.




